In FX trading, understanding macroeconomic indicators is critical as a country’s currency strength is often dictated by the health of the underlying economy. Strong economic data can sharply move the FX pair in a direction that the technical indicators often might be unable to predict. While economists tend to look at lagging indicators such as GDP growth, for traders, it is important to look at leading indicators that predict economic data ahead of time. Among leading economic indicators, Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) stands out as the most widely used measure. In fact, all types of traders, whether they are scalpers, momentum traders, or investors, extensively track the monthly PMI of the currency’s underlying country. This means that almost every market participant will react to any surprises in the PMI data, making the impact of this indicator all the more potent.
What is PMI?
So let us understand this indicator in detail. PMI is essentially a survey conducted by the Institute for Supply Management (ISM). The survey is conducted on a monthly basis and is sent out to a large number of companies — 400 companies in the US belonging to 19 specific industries — that are the major contributors to the economy. These industries are weighted by the amount of their contribution to the national Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
There are five main subsections of this survey as follows:
- Employment
- New Order
- Supplier Deliveries
- Production
- Inventory Levels
The ISM assigns equal weight to each of these subsections. The survey asks the senior executives from various companies about their outlook on the business conditions for each of the above-mentioned subsections in the coming month. They can respond with one of the three choices: improving, deteriorating, or not changing. Each of the subsections mentioned above measures a different aspect of the economy and supply chain. Hence, the expected changes in each subection are valuable indicators in assessing the overall health of the economy in the coming month.
So, for example, a senior executive of a steel manufacturing company will be asked if he expects the new orders for steel products to his firm to increase, decrease or remain at roughly the same level. This will help in determining the demand for steel products in the future. Similar assessments can be made based on the answers to other subsections.
Measuring PMI
The ‘headline’ PMI number, which is the weighted average of all sections and industries as explained above, always lies in the range of 0 to 100. In this range, 50 indicates a neutral level which implies no major changes are expected in the economy. Any number higher than 50 predicts an improving outlook for the economy, while any number below 50 portends a contraction. Needless to say, the higher the number above 50, the stronger the economy is expected to expand and vice-versa.
The formula for PMI is as follows:

where P = % positive answers, N = % negative answers and C= % neutral answers.
Apart from ISM, other institutions such as IHS Markit conduct PMI surveys for countries other than the US and publishes them monthly.
What does PMI mean for currencies?
The strength of a currency has a very strong correlation to the economy of the nation. An expanding economy means more investments into the economy, which would happen via the domestic currency leading to more inflows and hence a rise in the value of the currency relative to others. So a strong PMI number will mean that the currency too will strengthen in the short-term.
The chart below shows the US PMI data from April 2020 till April 2021.
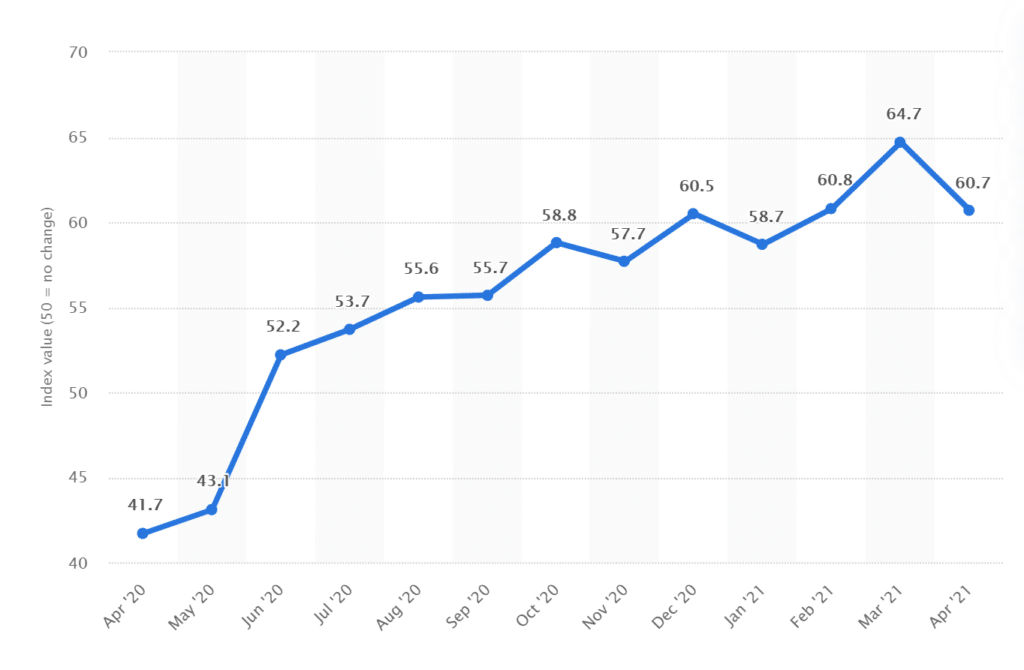
To understand this, let us discuss an example as shown in the chart below. The US PMI number is announced on the first day of the month, typically around the start of equity market trading for the day.
As soon as the PMI data was released, we can see that the EUR/USD saw a sharp fall in a matter of few minutes. This is because the PMI data was much stronger than expected, which meant the US economy was expanding at a faster rate. As a result, USD strengthened against EUR, and hence the forex pair saw a sharp fall.
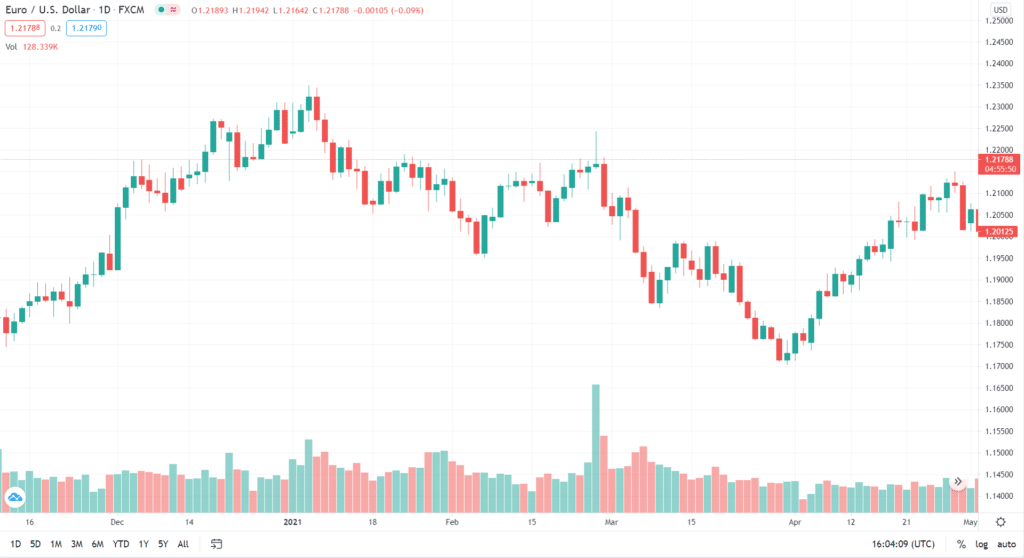
Similarly, USD strengthened against all other currencies as well, and those forex pairs too saw a large move.
One must keep in mind that analyzing PMI numbers is not simple as it looks. There is no doubt that a higher PMI number means a stronger economy, but at times central banks such as the Federal Reserve in the US are not comfortable when the economy expands too fast. A rapid expansion in the economy may be accompanied by inflation as a fast rise in demand for goods would most certainly mean an increase in prices as well.
While a low level of inflation is not a cause of worry, if inflation starts rising consistently with the economy it does not bode well. Higher inflation means the purchasing power of the currency is decreasing and this could result in a weakening impact on the currency. So one must assess the situation carefully while trying to use PMI to build FX trading strategies. It is a common understanding that a PMI number from 50 to 60 is generally perceived positively. But a number higher than 60 is uncommon and might suggest that the economy is expanding at an unsustainable pace which in turn could have a negative impact on the currency.
On the other hand, a PMI number below 50 most certainly means that the economy is contracting and that is a warning sign for recession. So a weak PMI number would almost always lead to the currency weakening.
PMI – A useful leading indicator for FX traders
As seen above, the main advantage of PMI over other economic indicators is that it’s a leading indicator and gives us information about where the economy is headed in the future rather than what has happened in the past. Hence it is widely tracked by all types of FX traders and has an outsized impact on currency pairs. However one should assess extreme cases before trying to formulate FX strategy or trade ideas based on PMI.