Imagine using any digital application free from censorship, that no one can shut down, has no downtime, isn’t owned by an individual, with one anonymous login and built-in payments.

Imagine using any digital application free from censorship, that no one can shut down, has no downtime, isn’t owned by an individual, with one anonymous login and built-in payments.
Well, this is the world of decentralized applications (dApps), which have taken the usage of cryptocurrencies to levels previously unimagined before.
A dApp is any type of crypto-based application running autonomously and trustlessly without any centralized intermediary. Decentralized applications rely on blockchain technology for data storage and smart contracts to facilitate functional logic.
With such an invention, users can do many things, from swapping different coins with fully-fledged exchange capabilities, having their own digital wallet to selling a range of art-related items and borrowing all without any human intervention.
Ethereum was the first blockchain to popularize this concept. Its most famous co-founder, Vitalik Buterin, saw that cryptocurrencies could lead to more complex application development aside from acting simply as money.
To this day, the majority of dApps are deployed using Ethereum. However, other blockchains competing for this dominance include Binance Smart Chain, Solana, Polygon, Avalanche, and Fantom.
So, let’s explore the main components of a decentralized application and the most popular types you will likely see.
Key elements of a dApp
The image below explains the distribution process of a decentralized app compared to a conventional one.
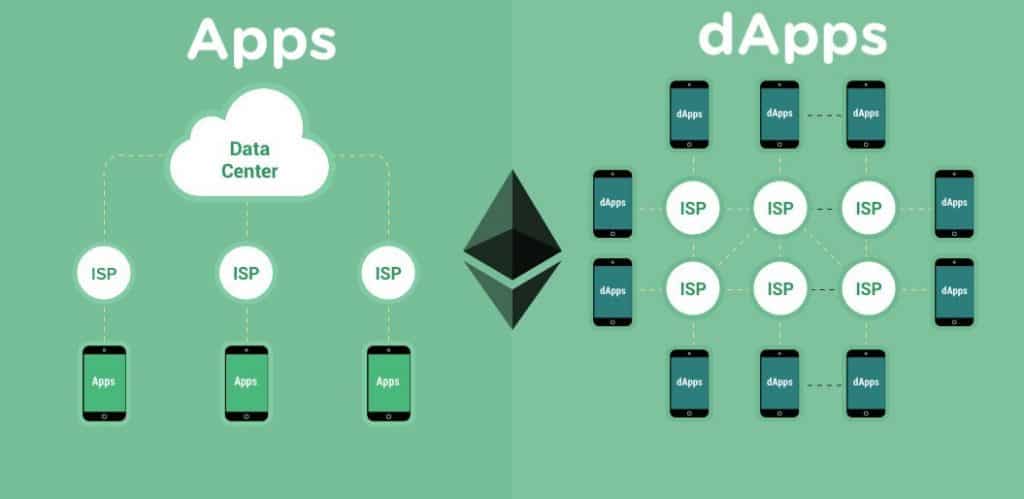
Regardless of whether the dApp is an exchange, borrowing/lending platform, social media platform, or wallet, these kinds of applications share similar characteristics:
- Open-source: This means the underlying codebase is publicly made available where anyone can verify, copy and modify it where necessary.
- Decentralized: It is now possible for such applications to function using a distributed network of nodes or computers instead of a centralized server.
Blockchains make the dApps cryptographically secure as all data is recorded and permanently stored. Moreover, a distributed network means no single point of failure exists, making such applications less vulnerable to technical problems.
Anyone can use these apps or build their own with some coding experience and enjoy the same benefits.
- Smart contracts: This is merely the programmed logic behind dApps that makes it possible to work autonomously. Each operation in the application is defined by a set of rules pre-coded into contracts that will execute certain functions once particular conditions are met.
- Anonymity: Unlike centralized systems where private data leakage is familiar, you can be entirely anonymous when using any decentralized application. You usually just need to connect your wallet, and you’re good to go.
We’ll now go over the most prevalent types of decentralized applications in cryptocurrencies.
Finance-based dApps
These are the most prominent types of dApps and form part of the DeFi (decentralized finance) movement. According to Defi Llama, at least $200 billion worth of value is locked in all DeFi protocols.
Such applications carry out a complex range of financial operations without relying on institutions like banks, exchanges, and brokerages.
These include lending and borrowing funds peer-to-peer (including lending to earn interest), trading derivatives, taking out insurance, sending payments, and even becoming a liquidity provider. Let’s list the typical kinds of dApps below.
- Lending/borrowing: These services allow users to lend out their tokens to earn interest. Conversely, you can borrow a range of coins with reasonable interest rates, flexible payment terms, and no credit checks (although you usually have to collateralize your loan with crypto).
Popular examples of these platforms include the likes of Oasis, Compound, and Aave.
- Exchanges/token swaps: Just as you can swap different coins on a platform like Coinbase or Binance, decentralized exchanges allow you to do the same but with data privacy, anonymity, and blockchain in mind.
Many of these facilities focus purely on token swaps (e.g., Uniswap). Others are aggregators (e.g., 1inch, Matcha) by sourcing liquidity from other exchanges.
These applications are also characterized by governance and utility tokens with various incentive mechanisms like staking, yield farming, and liquidity provision.
- Trading/prediction markets: Here, you can trade with leveraged positions (e.g., dYdX). Also, you can bet on the outcomes of sports, economics, and other world events with prediction markets (e.g., Polymarket, Augur, etc.)
- Insurance: These platforms specialize in offering insurance to smart contract and exchanges hacks without any centralized entity (e.g., Nexus Mutual)
- Investments: Facilities in this regard are geared towards making you money. They can range from crypto-based index funds (as with Index Coop) to lottery bonds on PoolTogether.
Art-based dApps
These applications focus on selling a host of art-related items, most commonly digital collectibles (artworks, images, videos, music, trading cards, etc.) being tokenized into non-fungible tokens.
Nifty Gateway, SuperRare, OpenSea, Rarible, and Foundation are some of the most known services for trading such items.
Other art-based dApps may include a music streaming platform like Audius that emphasizes providing inventive ways for creators to get paid without, again, any of the go-betweens you’d expect normally.
Gaming-based dApps
Gaming-based decentralized applications are part of the blockchain gaming sector, which are video games revolving around the cryptographic tokenization of a range of in-game assets that players trade amongst each other.
This has recently led to a renewed interest in virtual worlds known as metaverses introducing whole new elements of playing, socializing, and earning.
In the spirit of decentralization, most of the money made with these apps goes more to the players (leading to the play-to-earn concept) and less to the game publishers. Illustrations of the most prominent gaming-based dApps include The Sandbox, Decentraland, Axie Infinity, My Neighbor Alice, and countless others.
Final thoughts
Of course, it goes without saying that dApps are far from perfect and are highly experimental. Developers constantly think of new ideas that may seem ludicrous at first but could lead to innovative products.
dApps have demonstrated the far-reaching capabilities of blockchain technology beyond just digital mediums of exchange. Thus, the applications we have covered only scratch the surface of what’s presently out there.
Nonetheless, while facing several teething issues right now, decentralized applications will likely reshape entire industries known for considerable corporate control and shift much of this power to the users behind them.



