Investment Thesis
- How much impact will market fluctuations have on your retirement investments?
- Why should you consider an IRA?
- Traditional vs. Roth IRA: Which serves you best in the long-term?
- The risk-reward potential with IRAs.
Market Background
Despite the market fluctuation being high in 2020, stocks still rule the roost when it comes to long-term investments. Although the price swings are higher with stocks, they have outperformed cash and bonds.
When seen for a period ranging from 1926 to 2016, they have given an annual return of 10% while bonds have delivered just around 5%.
It is best to continue investing right through the volatility for those who have more than a decade until they quit work. In fact, when prices hit rock bottom during market pullbacks, you will find them the best investments that give back more long-term profits.
The Idea Behind The Investment
IRA (Individual Retirement Account), as the name suggests, helps in longstanding savings for individuals with high growth potential and without being encumbered by taxation. This account is usually started in a financial institution. Some important facts why an IRA is a good investment include:
- You can increase your returns in a tax-deferred way. That is, you will not have to pay tax on the income you earn from the funds until the time when you withdraw the gains.
- The funds funneled towards paying for the taxes will accumulate in your funds and compound. This ensures your gains are maximized in the end.
- When compared to a taxable account, a tax-deferred account will grow faster. For instance, let us assume you contribute $5000 towards a traditional IRA (tax-deferred) and the same towards a taxable investment. Both give you around 8% returns annually. However, with tax paid on the earnings, in 30 years, the amount increases to $419,000, but with an IRA, you get $611,700 approximately, which is $190,000 more.
IRA: Main Types To Know
Individual retirement accounts are of two main types, namely:
- Traditional. This type of IRA delivers tax-deferred gains. The amount you contribute in this account are tax-deductible, and all earnings continue increasing tax-free until you pull them out when you retire. Further on quitting work, the taxes are lower than the pre-retirement phase, so the deductions made are less.
- Roth. In this category, you pay the taxes for the contributions, and the amount increases without further taxes, and removal can be done tax-free too. But you need to meet specific conditions to enjoy the benefits offered.
According to estimates by financial experts, you will require about 85% of your current earnings when you retire. While plans like 401k help to increase your savings, they alone are not sufficient. An additional IRA can help towards:
- Providing supplementary savings
- Make use of diverse investment options.
- Increase your returns through the tax benefits that IRA offers
Fundamental Perspective On IRA
With an IRA, you are exempt from taxes on the earnings you make from investing the fund in stocks, ETFs, mutual funds, etc. Compared to a typical brokerage account, an IRA gives you a tax-free dividend. Selling an investment made through IRA at a profit will increase its value and still be tax-free until you withdraw funds from the IRA.
Being tax-deferred, the funds contributed to the traditional IRA are liable to tax deduction in the contributing year provided you meet the eligibility criteria. Without an employer-sponsored plan, this deduction is applicable, but if you already have a workplace plan, the deduction can be restricted. Find below the 2020 AGI threshold levels:
| Tax Filing Status | You AGI must be lower than this for a full deduction | You AGI must be lower than this for a partial deduction |
| Single or head of household | $65,000 | $75,000 |
| Married filing jointly | $104,000 | $124,000 |
| Married filing separately | $0 | $10,000 |
In the Roth IRA, you contribute to the account using after-tax money. Thus, any withdrawals are tax-free. There are other benefits, such as:
- It is easy to make early withdrawals as you will not have to worry about taxes or penalties as with the traditional account.
- The amount remains RMD (Required Minimum Distribution)-free. So, you can allow your money to increase without any limit. This has benefits, like:
- The sustained growth of your money is ensured.
- You get to avoid selling during a market downturn.
- You can convert your current traditional IRA plan to the Roth form by the backdoor Roth IRA method. But you have to pay tax on the deductible cash deposits and the gains.
Comparing To Benchmarks

For the best long-term savings, 401k plans are considered the standard by many. But an IRA also offers several advantages, such as:
- It allows you to invest in a diverse range of instruments, including ETFs and mutual funds, instead of the limited choices available with a 401k plan.
- With IRA, some exemptions to withdrawal, like using the amount for the purchase of a home or college fees are present.
- Despite the fact that the traditional and Roth types are beneficial in their own way. Deciding on the type that is best, rely on:
- Your present tax level and the one you will have when you retire matter much. If it is higher on retirement, the Roth will be more beneficial.
- If you are dealing with RMDs, you need to know how to deal with low liquidity alternative assets in your portfolio.
Risk Reward Potential
Regardless of the IRA category you pick, you can limit the risk exposure and maximize your gains. Here are a few tips:
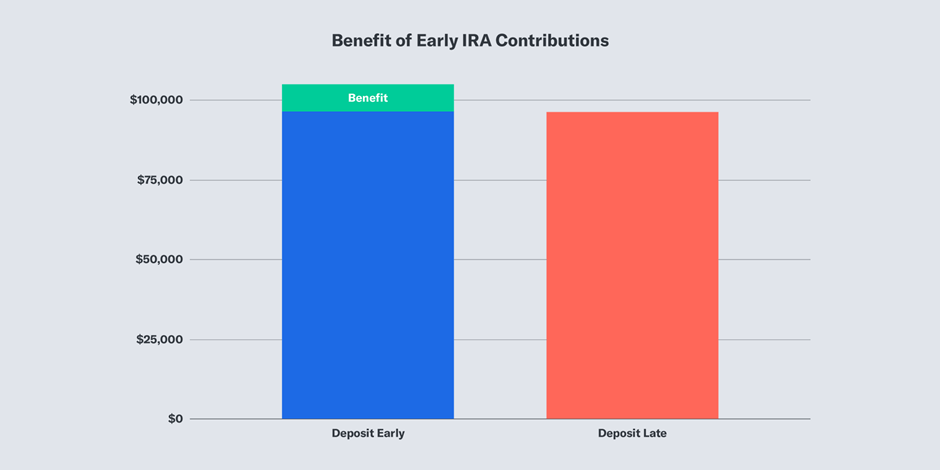
- Start saving early, even if you can make only small contributions. This is because the tax benefits with both account types help in compounding your money, resulting in a bigger balance.
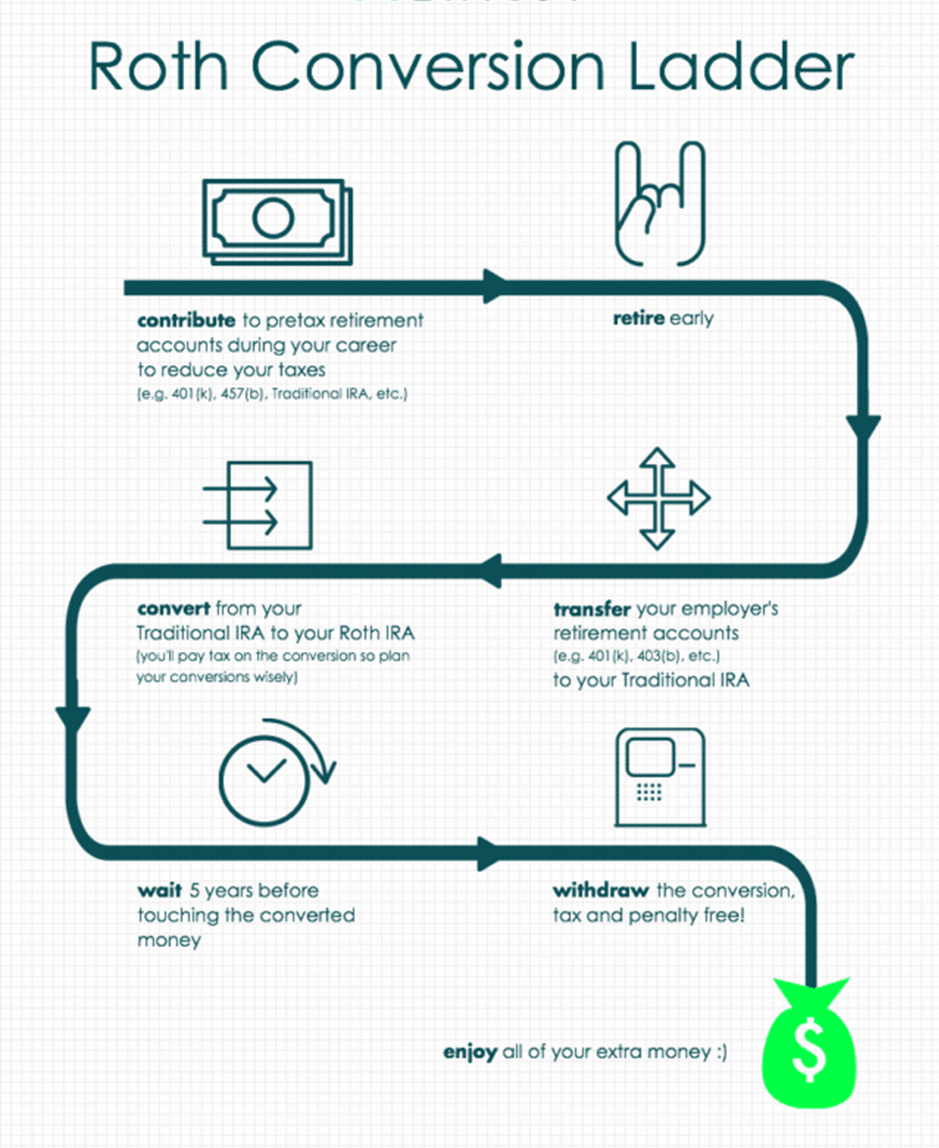
- Consider switching over from the Traditional to Roth account. This is beneficial if you have a higher tax level when you retire.
- Make contributions during the beginning of the tax year, so your funds get compounded for a longer span. Or make small contributions on a monthly basis, which will also help in maximizing profits.
- Ensure you add a beneficiary for the account as it helps the account to continue growing even after your time. Your spouse or minor child, or a disabled dependent can take lifetime distributions instead of a one-time payment. It is best to divide the account into separate accounts for each of the beneficiaries.
Conclusion
Regardless of the volatility and the account type, you need to know how to balance the time available until you retire and the risk level you can afford to reap high profit from your investment. Here are two scenarios to mull over
When you select conservative savings at an early age, the growth of the savings will not be on par with inflation giving you lesser returns.
If your savings approach is too aggressive, especially when you are near your retirement, there is a high risk of losing your savings to a volatile market. This will lead to a reduction in your asset value, and very few opportunities open for recovering the loss.

